Board of Directors Message
- We bring power to remote areas of the country both in the form of rentals and in the form of direct purchases
- We realize that we are not alone and we need the support of all parties and need the help of a reliable workforce
- We realize we live in the world, so we are proud to participate in renewable energy, both with orc, organic rankien cycle and other activities
President Director
Narendra

Oil Platform
A gas engine is an internal combustion engine that uses gas as its fuel. Unlike gasoline or diesel engines that use liquid fuel, gas engines burn a mixture of gas and air in the cylinder to produce power. Commonly used gases include natural gas, propane, and biogas.
Here are some of the main characteristics of gas engines: However, nitrogen oxide emissions can be a problem.Uses: Used in a variety of applications, including power generation, space heating, pumps, and vehicles. Maintenance: Maintenance is relatively easy, although certain components require special attention.T here are different types of gas engines, which are classified based on factors such as operating cycle (e.g. Otto cycle or Brayton cycle), cylinder configuration (e.g. single cylinder or double cylinder), and cooling method. The choice of the right type of gas engine depends on the specific needs of the application.
Diesel Engine
A diesel engine is an internal combustion engine that uses the compression ignition process to burn fuel. Unlike a gasoline engine that uses a spark plug to ignite combustion, a diesel engine ignites due to heat generated from the compression of air in the cylinder. Diesel fuel is sprayed into the hot compressed air, causing spontaneous combustion. Here are some of the main characteristics of diesel engines: There are various types of diesel engines, which differ in terms of size, cylinder configuration (e.g., inline, V, or radial), and fuel injection system. The choice of diesel engine type depends on the application and its specific needs.

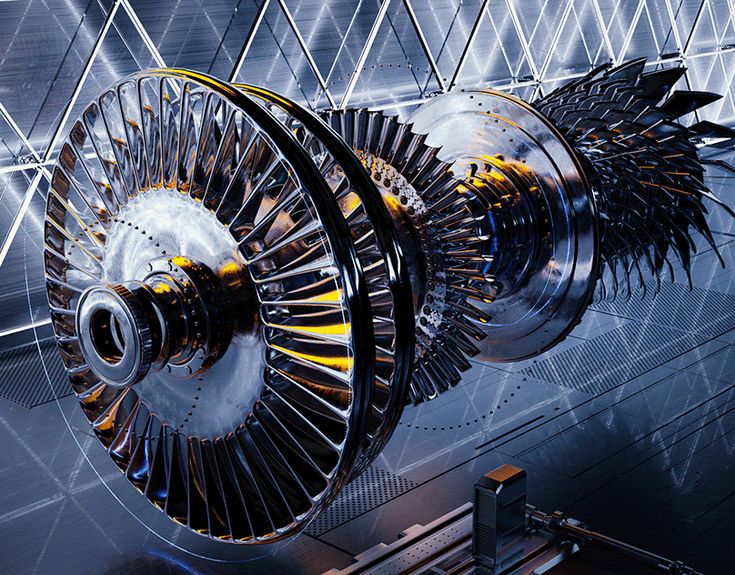
Steam Turbine
A steam turbine is a rotating machine that converts heat energy from high-pressure steam into mechanical energy. High-pressure steam is passed through the blades of the turbine, causing the blades to rotate and generate rotary power. This rotating power can then be used for various purposes, such as turning electric generators to produce electricity, or turning pumps and compressors.
Here are some of the main characteristics of steam turbines:
- Working Principle: Based on the principle of converting heat energy from steam into rotational kinetic energy. The expanding steam pushes the turbine blades, causing rotation.
- Efficiency: Relatively efficient, especially at large capacities and high speeds. Efficiency is affected by steam pressure and temperature.
- Uses: Used extensively in steam power plants, process industries (e.g., paper mills, oil refineries), and marine vessels.
- Sizes: Available in a wide range of sizes, from small turbines for industrial applications to giant turbines for power generation.
- Type: There are different types of steam turbines, such as impulse turbines and reaction turbines, which differ in design and how the turbine blades work.
Maintenance: Requires regular maintenance to ensure its performance and safety.
In short, steam turbines are very important machines in energy conversion, converting heat energy from steam into useful mechanical energy.
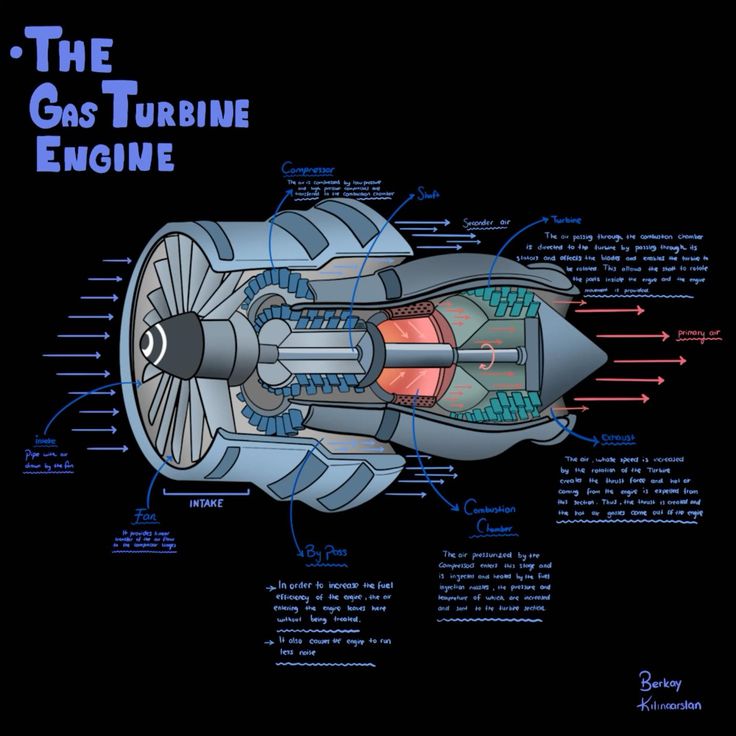
Gas Turbine
Gas turbines are internal combustion engines that use the Brayton cycle to convert heat energy from fuel combustion into mechanical energy. Unlike piston engines, gas turbines use a continuous flow of hot gas to rotate the turbine. The fuel, usually natural gas or liquid fuels such as kerosene, is burned in a combustion chamber, and the resulting hot gas is then passed through the turbine to generate rotating power.
Here are some of the main characteristics of gas turbines:
- Working Principle: Uses the Brayton cycle, which involves compression of air, heat addition through combustion, expansion of hot gases through the turbine, and exhaust.
- Efficiency: Efficiency increases with increasing pressure ratio and inlet turbine temperature. However, its thermal efficiency is generally lower than that of a diesel engine or steam turbine of the same capacity.
- Power to Weight Ratio: It has a high power to weight ratio, making it ideal for applications where weight and size are important considerations, such as aircraft and portable power plants.
- Uses: Used extensively in a variety of applications, including power plants, aircraft (as jet engines), marine vessels, and gas pumps.
- Types: There are different types of gas turbines, such as axial turbines and radial turbines, which differ in their design and operation.
- Emissions: Produce emissions, including nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), and particulates.Modern technology seeks to minimize these emissions.
- Maintenance: Requires regular maintenance to ensure its performance and safety.
Gas turbines are robust and relatively simple machines, suitable for a wide range of applications that require high power and a good power-to-weight ratio.

Our Quality Assurance
At PT Blue Technology Indonesia, quality is at the core of everything we do. We are committed to delivering reliable, efficient, and sustainable energy solutions that meet international standards.
1.ISO-certified systems
ISO-certified systems that ensure safety, consistency, and excellence
2.Team Professionals
A dedicated team of trained professionals focused on innovation and precision
3.Continuous investment
Continuous investment in technology to enhance environmental responsibility and performance

Our Experience
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry's standard dummy text ever since the 1500s.
Insight of Company
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry's standard dummy text ever since the 1500s.





